Summarize This Article:
Summarize This Article:
Sustaining a brachial plexus injury can be a shock. One day you’re riding high; the next day you’re in debilitating pain and challenged by everyday tasks. The diagnosis can feel overwhelming, but you can take comfort in receiving answers to your questions and finding a qualified care team to get you on the road to recovery.
The good news is many treatment options are available for a brachial plexus injury, and most patients regain full function in their arm and shoulder.
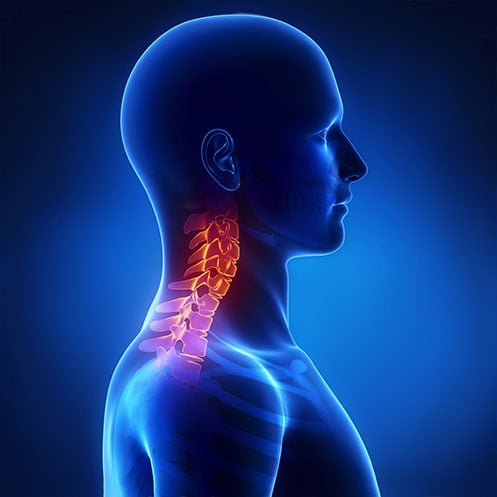
The brachial plexus is located at the top of the neck and extends through the shoulder and hands.
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves consisting of five terminal branches that control movement and sensation to the shoulder, arm, wrist, and hand by sending signals from the spinal cord.
The most common cause of brachial plexus injury is trauma to the shoulder, which can occur at birth or from falls, car accidents, sports injuries, piercing wounds, or surgical mishaps. Tumors and radiation therapy can also damage nerve tissue, leading to a brachial plexus injury.
Like any health condition, brachial plexus injuries vary in severity. Some cases cause mild discomfort and may heal on their own. Serious brachial plexus injuries can cause chronic pain, loss of function or paralysis, and a decreased quality of life. It may take several years and multiple courses of treatment to heal.
A brachial plexus injury can cause debilitating chronic pain in the shoulder, neck, back, chest, wrist, and arm. The worse the nerve damage is, the further throughout the body the pain can reach. It’s often described as a constant burning sensation or feeling of weakness or numbness. Patients can work with their care team to form a treatment plan and manage pain.
 Symptoms of a brachial plexus injury can vary depending on the extent of the nerve damage. Common symptoms include:
Symptoms of a brachial plexus injury can vary depending on the extent of the nerve damage. Common symptoms include:
A doctor can diagnose you with a brachial plexus injury by completing a physical exam, reviewing your symptoms, and using diagnostic tools like an x-ray, MRI, CT scan, nerve conduction study, or electromyogram.
A brachial plexus injury is not an emergency but should be evaluated and treated promptly. If the injury is unlikely to heal on its own, surgery should be done within six months of the initial injury.
Reconstructive surgeons, plastic surgeons, orthopedic surgeons, neurosurgeons, and rehabilitation specialists are the most qualified doctors to treat brachial plexus injuries. Dr. Elkwood is an international expert in nerve reconstruction surgery for patients who suffer from brachial plexus injuries.
Leaving a brachial plexus injury untreated can result in chronic pain and lifelong disability. Mild cases may heal on their own, but it’s recommended to seek treatment promptly for the best outcome.
Anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy can help restore function and treat pain for mild brachial plexus injuries. Surgical nerve reconstruction procedures such as decompression, neurolysis, nerve graft, nerve transfer, and muscle transfer may be required to treat severe nerve damage.
When patients don’t get relief from medication and physical therapy, surgical procedures can cure or significantly improve the brachial plexus injury. A study by surgeons at The Institute for Advanced Reconstruction found that muscle transfer procedures are particularly effective. All patients experienced a meaningful decrease in pain following treatment, 33 percent were able to decrease their pain medication use, and 50 percent were able to discontinue the use of all pain medication. Patients typically regain 90 to 100 percent of the arm’s strength and functionality within two years of surgical treatment.
Many cases of brachial plexus injuries require surgery to restore function, mobility, and sensation to the arm and relieve pain. Severe instances involving paralysis may even require multiple surgeries over time.
Brachial plexus injuries can take several weeks to months to heal, depending on the severity. If the patient must undergo surgery, they should rest and restrict arm activity for at least four weeks after the procedure. It’s recommended that patients complete physical therapy on a regular basis for several months to support healthy nerve and muscle recovery.
Request an Appointment or visit the Center for Brachial Plexus Injuries online to learn more.