Summarize This Article:
Summarize This Article:
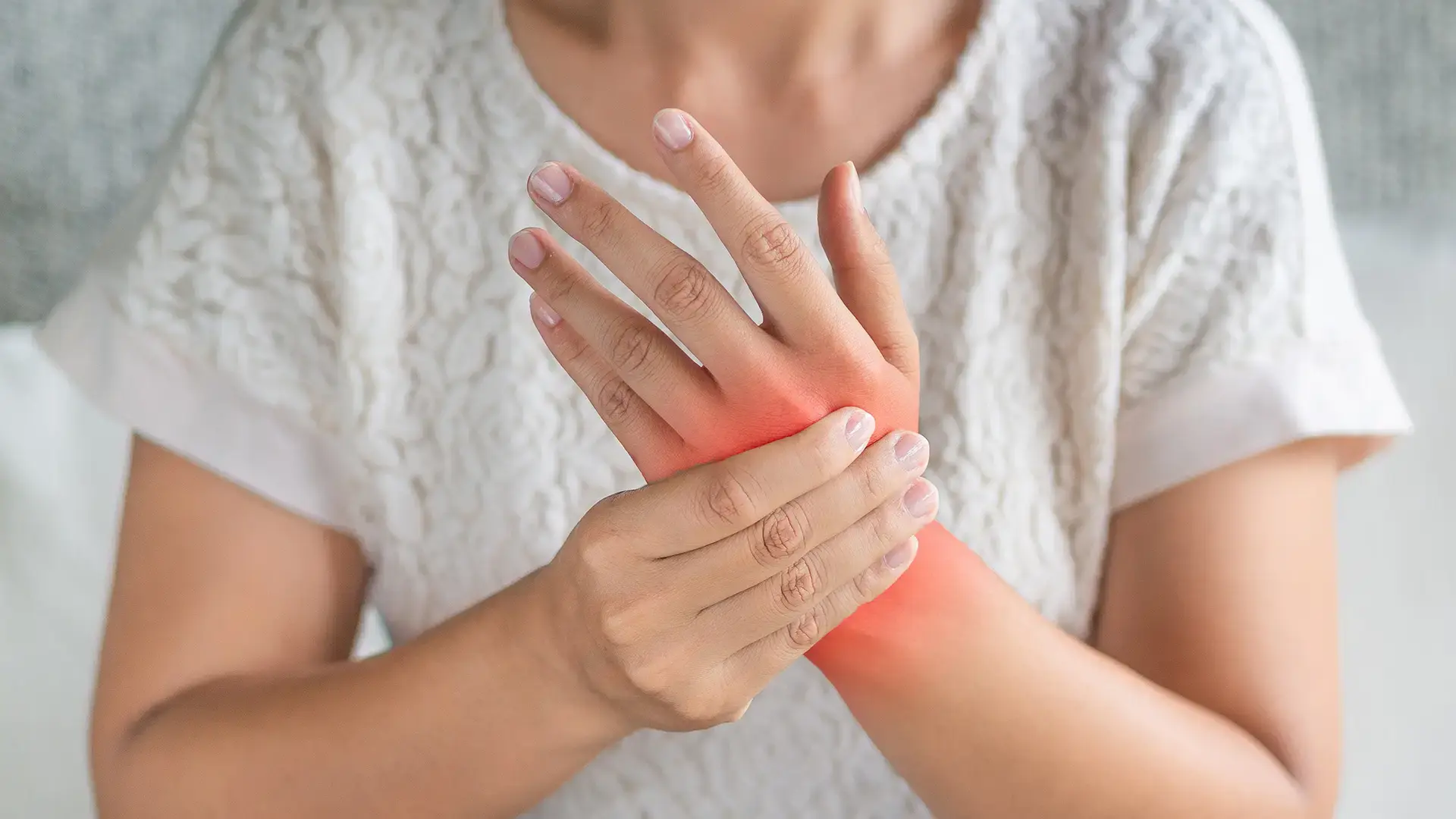
You may have never heard the term scaphoid, but that doesn’t mean it isn’t an essential bone in the body. In fact, a scaphoid fracture is one of the most common types of wrist fractures—and one of the most commonly missed. Based in New Jersey, The Center for Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery serves patients throughout the region with advanced care for hand and wrist injuries.
“Because of its unique location and blood supply, the scaphoid bone is especially prone to complications if a fracture is overlooked or left untreated,” explains Dr. Ajul Shah, a board-certified hand and upper extremity surgeon at The Center for Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery.
The scaphoid is a small, boat-shaped bone on the thumb side of the wrist. It plays a key role in wrist movement and stability. The scaphoid bone is most commonly fractured as a result of trauma, such as when someone falls and tries to catch themselves with an outstretched hand. Athletes, especially those in contact or high-impact sports, are also at increased risk.
Scaphoid fractures can be especially challenging due to the limited blood supply in this area, which may delay healing and increase the risk of a non-healing fracture, or nonunion, potentially necessitating revision surgery.
Scaphoid fractures can be tough to identify because you may only have minimal swelling or bruising rather than severe wrist pain. But be careful not to mistake this type of fracture for a sprain.
Common scaphoid fracture symptoms include:
To diagnose a scaphoid fracture, your doctor will start with a physical exam followed by imaging tests such as X-rays. In some cases, MRI or CT scans are used to find subtle fractures or to monitor healing.
“We often see patients weeks or even months after the injury because symptoms were mild or misdiagnosed,” warns Dr. Shah. “But when we catch a scaphoid fracture early, we can often avoid complications and preserve wrist function without more invasive surgery.”
Treatment for a scaphoid fracture depends on the severity, type of scaphoid fracture, and how long the bone has been injured. In some cases, conservative care is enough, but often, fractures require surgical intervention to guarantee proper healing.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatment options can help stabilize the bone and reduce inflammation while the body heals naturally.
Non-surgical treatment methods may include a combination of:
However, conservative care isn’t enough for all fractures, especially if the injury is more severe or diagnosed later.
Surgery may be recommended for displaced fractures (when bones have moved), those with poor alignment, or cases that don’t respond to non-surgical care. Timely surgical intervention can also prevent complications such as nonunion fractures, which occur when the bone fails to heal correctly.
At The Center for Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery, our fellowship-trained surgeons perform advanced microsurgical procedures tailored to each patient’s needs, including:
So, how long do scaphoid fractures take to heal? Healing timelines depend on the severity of the fracture and the treatment method used.
Recovery can take longer after nonunion or revision surgery, but with proper care and rehabilitation, you should regain total function.
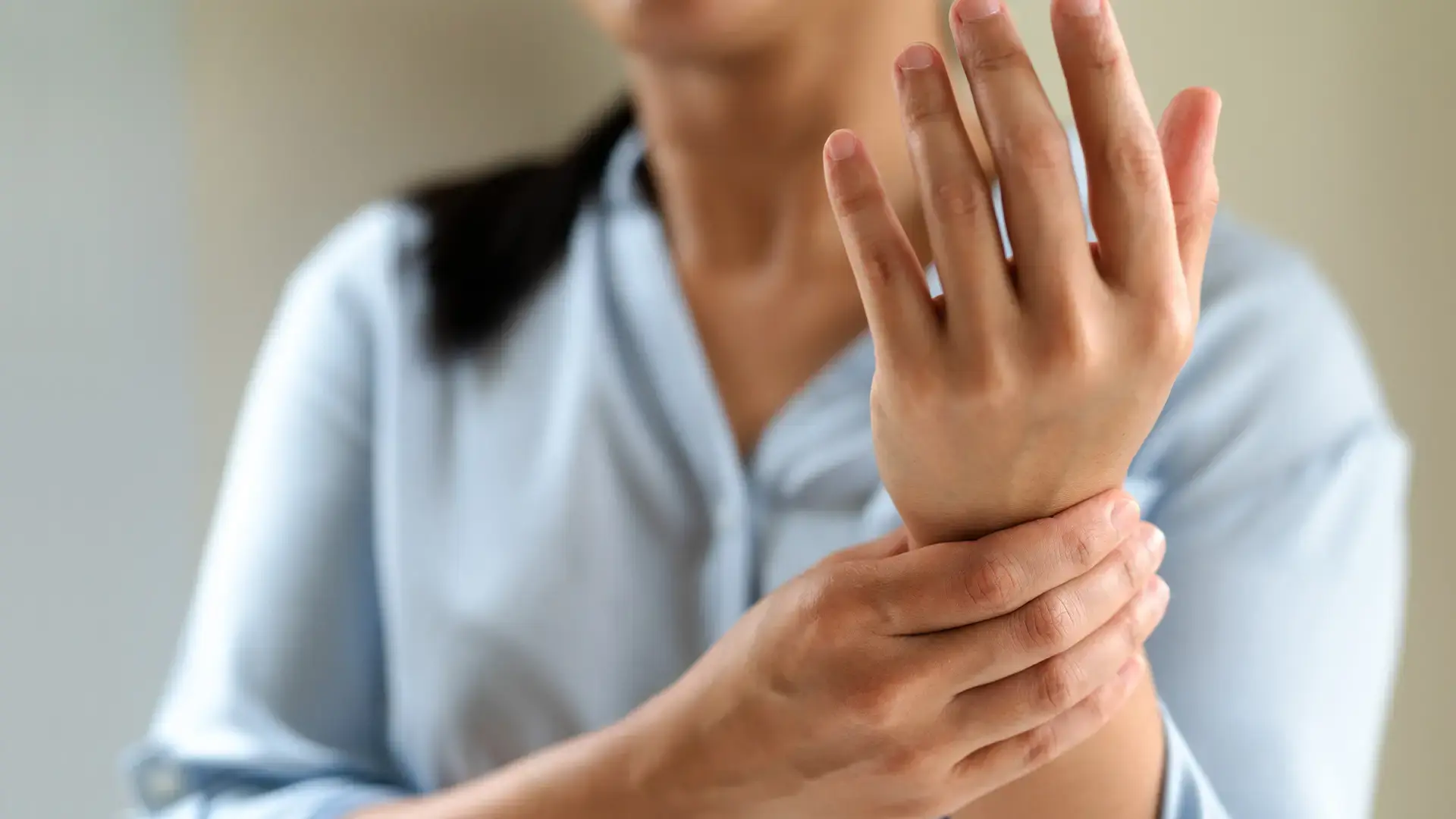
Do you have persistent wrist pain following a fall? Then it’s time to talk with a hand specialist, especially if you're recovering from a previous wrist injury that hasn’t fully healed. Remember: Early diagnosis of a scaphoid fracture leads to better results and lowers your risk for complications.
“The scaphoid might be small, but the impact of a fracture can be significant if it goes untreated,” reminds Dr. Shah. “With the right care, we can help patients recover full wrist function and avoid chronic pain or limited motion.”
1. What are the symptoms of a scaphoid fracture?
Common signs include pain or tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist, especially after a fall. You might also notice swelling, reduced grip strength, or discomfort with pinching or twisting motions. Scaphoid fractures are often confused with wrist sprains, so early evaluation is essential.
2. Can a scaphoid fracture heal without surgery?
Yes, in some cases. If the fracture is non-displaced (meaning the bone hasn’t shifted), it may heal with immobilization using a cast or splint. However, fractures in certain areas of the scaphoid, or those diagnosed late, may have a higher risk of not healing without surgical support.
3. How long does it take to recover from a scaphoid fracture?
Healing time varies based on the severity and treatment method, which includes:
4. What happens if a scaphoid fracture doesn’t heal properly?
When the bone fails to heal—a condition known as a nonunion—you may experience chronic pain, decreased range of motion, or weakness in the wrist. Nonunions often require revision surgery, which may involve bone grafting or internal fixation to restore proper function and prevent long-term joint damage.
5. When should I see a hand specialist?
If you have persistent wrist pain following a fall, especially on the thumb side of the wrist, it’s best to see a specialist—even if the injury feels mild. Early diagnosis leads to faster healing and fewer complications.
The Center for Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery treats chronic pain in hands, wrists, arms, and shoulders, including hand, wrist, arm, and shoulder arthritis, nerve injuries, and other common causes of chronic hand pain.
If you are ready to treat your scaphoid fracture, book an appointment with Dr. Shah and the care team in New Jersey at The Center for Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery, part of The Institute for Advanced Reconstruction.


.png)
.webp)