Summarize This Article:
Summarize This Article:
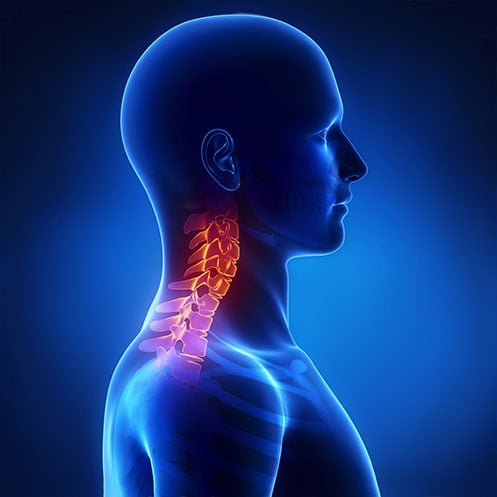
Neuropathy, also known as peripheral neuropathy, can be a very challenging and uncomfortable condition to live with. It occurs when the peripheral nerves that carry messages between the body and the brain become damaged or dysfunctional and can be caused by various factors such as diabetes, chemotherapy, infections, or injuries. The symptoms of neuropathy, such as numbness, tingling, or burning sensations, can be difficult to manage and can greatly impact one's quality of life. That's why seeking professional advice from a healthcare provider before self-diagnosing or treating symptoms of neuropathy is essential.
If you are experiencing symptoms of neuropathy, it's important to know that you're not alone. We've compiled a list of frequently asked questions to provide you with a better understanding of what neuropathy is, the various types and stages of neuropathy, and how neuropathy is treated to help you navigate your journey to a better quality of life.
 Currently, there is no known cure for most types of neuropathy, but treatments can help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. Neuropathy can sometimes go away on its own, but this depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Currently, there is no known cure for most types of neuropathy, but treatments can help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. Neuropathy can sometimes go away on its own, but this depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
A neuropathy doctor will typically conduct a physical examination, review your medical history, and perform several tests, including nerve conduction studies and Electromyography, to help diagnose neuropathy.
Yes, there are six different variations of neuropathy:
Peripheral Neuropathy: It is the most common type of neuropathy and affects the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. It can affect any body part with nerves, including the feet, legs, hands, arms, and even internal organs like the heart or digestive system.
Focal Neuropathy: Affect specific nerves or groupings of nerves in any part of the body. These types of nerve damage are usually caused by trauma to a single nerve (like carpal tunnel syndrome) but can also be due to inflammation, motor neuron diseases, or tumors.
Autonomic Neuropathy: It affects nerves that control involuntary body functions like digestion, blood pressure, bladder function, and sexual response.
Diabetic Neuropathy: It happens when high sugar levels injure nerve fibers throughout your body. Diabetes can damage any part of your nervous system – autonomic nerves, motor nerves, and sensory nerves.
Hereditary Neuropathy: It is a disorder caused by genetic mutations passed down from parent to child. More than 80 different hereditary nerve disorders have been identified so far.
Alcohol Neuropathy: It is nerve damage caused by excessive alcohol consumption over a long period. Most patients diagnosed with alcoholic neuropathy are aged 40-60 years. This condition affects the peripheral nervous system, causing pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness in the hands and feet.
Yes. Neuropathy is classified according to the severity of your symptoms. It’s important to note that not all patients will experience all stages of Neuropathy; some may only notice mild or moderate symptoms throughout their lives, while others may progress more rapidly.
There are no neuropathy symptoms yet, but the nerve damage has already begun. The damage is usually identified through physical examination and tests done on the nerves, such as nerve conduction studies.
The onset of numbness or tingling sensations in the feet or hands characterizes mild Neuropathy. There may also be some mild pain and weakness in the affected areas. Although these symptoms can be distressing and uncomfortable, they typically do not significantly affect daily life.
Moderate Neuropathy begins when the symptoms become more pronounced and impact daily life. In this stage, patients may experience significant limb pain, muscle weakness, reduced mobility, and difficulty with tasks like buttoning a shirt or gripping objects firmly.
Neuropathy's final and most advanced stage is when symptoms become debilitating for patients. Individuals may experience severe pain that cannot be treated with conventional medicine or difficulty completing basic tasks due to significant muscle weakness or loss of sensation in their limbs. In extreme cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to manage symptoms.
Neuropathy treatments in New Jersey may include medication, physical therapy, acupuncture, and lifestyle changes such as exercise and healthy eating habits. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan.
The most effective treatment for neuropathy depends on the condition's underlying cause. In some cases, treating the underlying cause can help alleviate the symptoms of neuropathy. For example, if neuropathy is caused by diabetes, managing blood sugar levels can help slow or stop nerve damage.
While surgery is not typically considered a first-line treatment, there are some surgical options for neuropathy that are highly effective in certain cases, such as:
Preventing neuropathy depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Overall, maintaining healthy habits like eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding exposure to toxins may reduce your risk of developing some forms of neuropathy. It’s also important to eat foods that help reduce nerve pain, such as lean protein, whole grains, and nuts.
Yes. Neuropathy can be a chronic condition, and while there is no cure, many people are able to manage symptoms and live normal, fulfilling lives. We’ve helped numerous individuals overcome the pain and discomfort of neuropathy by treating the source of the condition, adjusting daily habits, and creating personalized treatment plans. You can learn more about treatment options for neuropathy by booking a consultation with a specialist at The Institute for Advanced Reconstruction.


